What is mean by polyphase system ? State advantages of polyphase and single phase system.
Polyphase System Explained: Advantages versus Single-Phase Systems
What is a Polyphase System?
Advantages of Polyphase Systems:
1. Higher Power Capacity:
For the same voltage and conductor size, a polyphase system can transport more power than a single-phase system. This is because the phases add together constructively, giving a greater peak voltage. This makes polyphase appropriate for industrial applications and long-distance power transmission.
2. Smoother Power Delivery:
The various phases of a polyphase system cancel out each other's pulsations, resulting in a smoother and more steady flow of power. This is advantageous for equipment that is sensitive to variations, such as electric motors and lighting systems.
3. Increased Efficiency:
Polyphase systems use less conductor material for the same amount of power transmission compared to single-phase systems. This is because the phases share the neutral conductor, lowering the total number of conductors required. Additionally, polyphase motors are often more efficient than single-phase motors, thus lowering energy usage.
4. Improved Motor Performance:
Three-phase motors, intended for use with polyphase systems, provide substantial benefits over single-phase motors. They create a continuous rotational torque, resulting to smoother operation, greater starting torque, and improved speed control. This makes them perfect for driving large machines and industrial equipment.
5. Reduced Flickering:
In lighting applications, single-phase systems may generate flickering when the voltage drops at particular times in the cycle. Polyphase systems, on the other hand, give a more steady voltage, resulting in flicker-free lighting, which is crucial for both comfort and safety.
6. Cost-Effectiveness:
Despite the initial greater cost of installing polyphase systems, their enhanced efficiency, fewer maintenance needs, and longer lifetime make them more cost-effective in the long term, particularly for high-power applications.
Single-Phase Systems: Not Always Outclassed
While polyphase systems provide various benefits, single-phase systems still have their place. They are easier and cheaper to install and maintain, making them appropriate for low-power applications in households and small enterprises. Additionally, several single-phase products, such as hair dryers and toasters, are particularly intended for single-phase systems and operate perfectly fine.
Choosing the Right System:
The decision between a single-phase and polyphase system relies on various criteria, including:
• Power requirements: Polyphase systems are better suited for high-power applications.
• Budget: Single-phase systems are often cheaper to install initially.
• Equipment compatibility: Make sure your equipment is compatible with the selected system.
• rules: Some places may have unique rules addressing the operation of polyphase systems.
By knowing the benefits and limits of both single-phase and polyphase systems, you can make the best option for your individual requirements.
Technical Details:
1. Mathematics of Phase Angles:
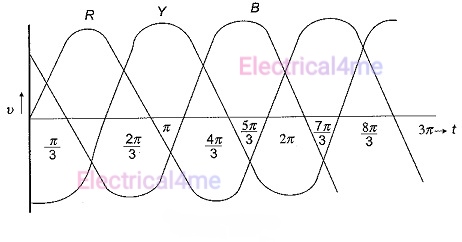
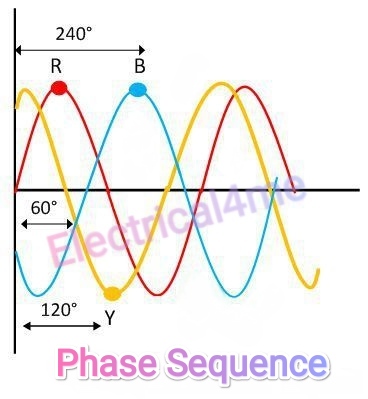
- Phase angle difference: In a three-phase system, each phase lags the preceding one by 120°. This amounts to a 2π/3 radians phase difference in mathematical terms.
- Vector addition: Phases may be represented as vectors, and their sum determines the net voltage and current. For balanced systems, vectors cancel out some components, resulting in a constant overall power, a crucial benefit.
- Power calculations: Three-phase power calculations entail factoring in phase angles and current/voltage correlations. Knowing formulae like P = √3VI (power in watts, voltage, and current) becomes vital.
2. Transformer Connections:
- Delta connections: Phases are linked in a closed loop, giving excellent fault tolerance and balanced voltages. Used for power distribution and motor applications.
- Wye connections: Neutral point connects to a common point, allowing reduced voltage for lights and certain appliances. But, single-phase loads might generate current imbalances.
- Open Delta: Used when one transformer in a Delta connection breaks, offering a temporary solution by utilizing two remaining transformers.
Real-World Applications:
1. Industry:
2. Transportation:
3. Renewable Energy:
Wind turbines and solar farms commonly link to the grid utilizing polyphase systems for efficient power transmission across long distances.
4. Smart Grids:
The dynamic nature of polyphase systems provides for improved management and monitoring of power flow in current smart grids.
Comparisons with Other Technologies:
1. DC Transmission:
More efficient for long-distance transmission owing to reduced line losses, but needs expensive converter stations at either end. Polyphase AC is preferable for shorter distances owing to quicker voltage translation.
2. High-Voltage Single-Phase:
Can transport more power with thicker conductors, but single-phase motors have downsides such pulsing torque and reduced efficiency. Polyphase gives smoother power and greater motor performance.
Future of Polyphase Systems:
1. Smart grid integration:
Advanced monitoring and control technologies will optimize power flow and increase reliability in polyphase networks.
2. Renewable energy integration:
Polyphase systems will play a crucial role in integrating variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the grid.
3. Advanced materials:
New conductor materials and insulation technologies will enable for more efficient and compact polyphase systems.
4. Microgrids:
Polyphase systems will be vital for decentralized power production and microgrid development, offering greater energy independence and resilience.